Gonarthrosis or osteoarthritis of the knee joint is a disease that cannot be completely cured.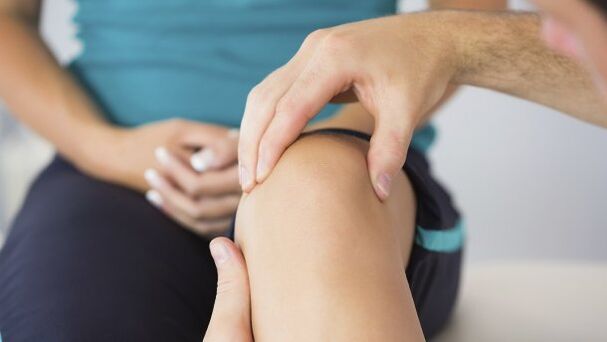 However, modern medicine has learned to stop the pathological destruction of tissues in the human body. Using effective treatments, doctors:
However, modern medicine has learned to stop the pathological destruction of tissues in the human body. Using effective treatments, doctors:
- relieve their patients of pain;
- eliminate discomfort while driving;
- slow the progression of the disease;
- considerably improve the quality of life of the person who requested them.
What is osteoarthritis of the knee?
The disease has several names for knee damage. It is often called knee osteoarthritis, arthritis deformans (DEformans osteoarthritis) and even arthritis, although the latter is more commonly used for rheumatoid pathologies.
The disease is progressive in nature, therefore, without professional help it often leads to serious complications. Due to its evolution, the cartilage tissue that lines the surface layer of the joint is affected. This becomes the reason for the malfunction of the capsule and the appearance of painful sensations.
According to one theory, osteoarthritis of the knee results from an increase in life expectancy. According to this theory, a person over 50 does not yet feel old and continues to be active at the same level. However, its joints fail, because they exhaust the resource given by nature.
Why does knee osteoarthritis develop?
Limited mobility makes walking, running and freedom of movement difficult. Unaccustomed to this, a person perceives these restrictions as a punishment. With the exacerbation of pathologies of the musculoskeletal system, even simple steps are difficult. After 50 years, the disease develops in one in two people. The most common causes of the abnormality in addition to age-related disorders:
- leg fractures affecting the knee joint area;
- knee dislocation, meniscus failure or injury;
- inflammation of the joint capsules (rheumatoid pathologies, gout, ankylosing spondylitis and others);
- failure of metabolic processes, joint weakness of a congenital nature;
- hereditary factor, genetic predisposition.
Knee osteoarthritis is also likely to develop in an older, overweight woman and a young man injured during exercise.
Symptoms of the pathology
The disease does not appear suddenly. Negative symptoms are mild at first and get worse over time. Almost imperceptible knee pain when walking becomes more intense with increased activity, while walking up the stairs. It seems that this manifests itself in the discomfort caused by prolonged immobility.
The body seems numb, and at the very beginning of movements, it tries to independently adapt to the new load. As soon as a person "disperses", the unpleasant symptoms of the disease disappear and the knee returns to normal mobility. This is when you need to see a doctor for an exam. By ignoring the diagnosis, a person puts themselves in great danger.
Gradually, the symptoms become more pronounced:
- the pain becomes continuous, now it does not go away during physical exertion;
- range of motion becomes scarce, the knee is limited, swells and increases in size.
Doctors say going to the clinic at an early stage opens up good prospects for treatment. The disease can be stopped without the use of expensive drugs and methods. With each new day of inactivity, the risks increase. In stage III, it becomes almost impossible to neutralize severe symptoms.
Diagnosis of knee osteoarthritis
At the first appointment, the specialist listens to the patient's complaints, clarifies the symptoms, examines the knee and directs the patient for an X-ray. In the early stages of changes, external signs are absent, in stages II and III:
- the outlines of the bones become coarser;
- joint capsules undergo deformation changes;
- the axis of the limb is bent and movement becomes limited.
On palpation, a crunch is often heard, it is worth moving the kneecap in a transverse direction. The pain becomes more pronounced. Thanks to the x-ray examination, you can clarify the diagnosis. The images make it possible to assess the degree of change, to differentiate the disturbances from other pathologies.
Treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee
When knee osteoarthritis is detected, an integrated approach to treatment should be used. Only then is lasting improvement possible. Here, an individual therapy plan is drawn up for each patient, where the author's traditional approaches and modern techniques are combined. When developing a treatment plan for osteoarthritis of the knee, the patient's age, history, lifestyle and history of correcting disorders of the musculoskeletal system are taken into account.
Drug therapy
Preparations for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee joint are selected from the following groups:
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- pain relievers;
- chondroprotective formulas based on hyaluronic acid (the purpose of which is to restore the integrity of the cartilage fibers in the damaged joint capsule).
Pharmaceutical companies produce a wide variety of drugs to treat this disease. Among them are creams, ointments, gel formulations, tablets, solutions for injections. Medicines are important when you need to quickly relieve acute pain, reduce the effects of the inflammatory process. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), steroids, and vasodilators are especially popular.
Manual joint therapy
Soft hand techniques allow you to gently and physiologically restore the natural anatomical relationships between internal structures. Since osteoarthritis occurs due to an overload of the knee, displacement and abrasion of cartilage, as well as an incorrect projection of the position of the bones in relation to each other, it is possiblecorrect the situation with manual therapy.
The doctor separates the badly placed structures in order to bring them together in the correct ratio. At the same time, the muscular and ligamentous corset is strengthened. The founder of the clinic uses the experience of Western colleagues and the author's methods in his work. This allows you to achieve a stable result that lasts for a long time.
Shock wave therapy
UHT is a proven method in Russian practice of treatment of knee osteoarthritis. The impact on the affected area is carried out through special equipment that generates acoustic signals with a pulse frequency of 2 to 4, 000 per session. Thanks to the material technique, it is possible to activate the blood circulation, improve the metabolism in the tissues and stimulate the regeneration of bone and cartilage fibers.
Di-Tazin therapy
Author's technique based on a combination of photosensitization, multicomponent electrophoresis and gentle manual techniques. It aims to restore the damaged joint, relieve pain and discomfort. It is supplemented by kinesiological procedures, taping, physiotherapy, blocking injections, the introduction of chondroprotectors and drugs based on hyaluronic acid into the joint. All this in one complex allows you to stop the destruction of the knee joint, eliminate pain and stimulate tissue renewal.
Plasmolifting
Safe and painless procedure. The doctor takes venous blood from the patient, processes it in a special centrifuge and, after separating the plasma, injects it into the damaged joint using an ordinary needle. It is recommended to follow the current sessions to consolidate the result. Plasmolifting helps relieve pain and inflammation, restore mobility of the joint capsule.
Taping
Applying tape (self-adhesive tape) in a direction specially chosen according to the location of the fibers of the damaged part. In case of illness, a wide tip is used. It relieves pain by relieving muscle tension. In case of swelling, a special lymphatic band is used, the rays of which are directed to the nearest lymph nodes.
Other treatments
In the clinic, specialists select contoured orthopedic insoles for patients with osteoarthritis of the knee joint. They help correct functional changes, relieve pain and evenly distribute the load on the legs. Strengthening the ligament system with home exercise therapy allows you to stabilize the position of the knee.